Regenerative Medicine: The Future of Healing
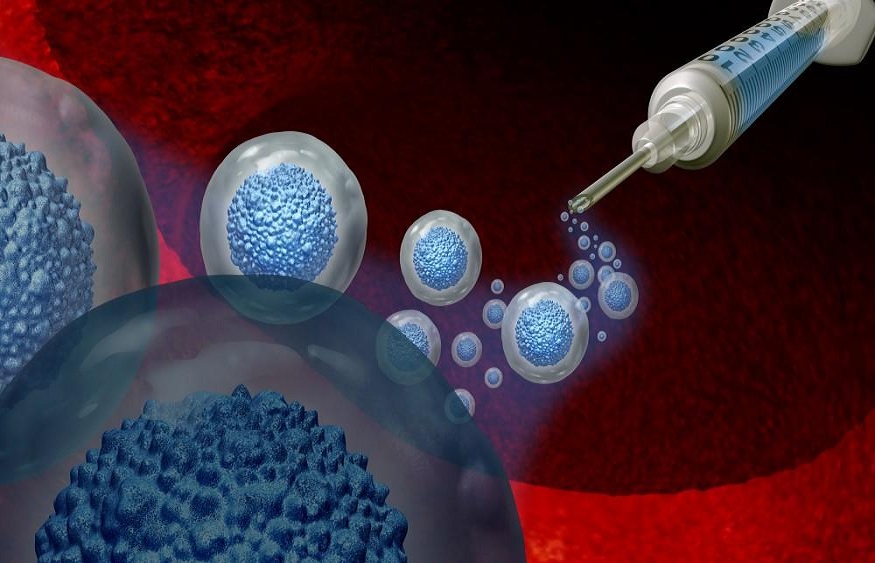
Imagine a world where your body could heal itself from severe injuries, chronic diseases, or even organ failure—not with a transplant or external aid but by activating its own natural processes. This is not science fiction; this is regenerative medicine. The concept sounds futuristic, but in reality, it’s a rapidly growing field that’s already changing the way we think about healthcare.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through what regenerative medicine is, how it works, and why it’s poised to revolutionize the medical world. We’ll keep it casual but dive deep enough to appreciate the incredible science behind it.
What is Regenerative Medicine?
At its core, regenerative medicine is all about harnessing the body’s natural ability to repair, replace, and regenerate damaged or diseased tissues. Unlike traditional treatments that focus on managing symptoms or replacing damaged tissues with transplants, regenerative medicine aims to restore normal function by stimulating the body’s own healing mechanisms.
This field is built on three key pillars:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Using undifferentiated cells that can transform into specialized cell types to repair or replace damaged tissues.
- Tissue Engineering: Creating functional tissues in the lab to replace or support failing tissues and organs.
- Biologics: Employing growth factors, cytokines, and other biomolecules to encourage tissue repair and regeneration.
How Does It Work?
The science behind regenerative medicine is as fascinating as it is complex. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Stem Cells to the Rescue: Stem cells are like the body’s raw materials—they have the unique ability to become almost any type of cell. Researchers harvest these cells from sources like bone marrow, fat tissue, or even umbilical cord blood. Once harvested, these cells are injected into the damaged area, where they differentiate into the needed cell type (e.g., muscle, nerve, or cartilage).
- Tissue Engineering: Picture a lab where scientists use 3D printing to create a scaffold for new tissues. These scaffolds are then seeded with cells and grown in bioreactors until they form functional tissues. This method has been used to develop skin grafts, blood vessels, and even parts of organs.
- Biomolecules: Sometimes, the body just needs a nudge in the right direction. That’s where growth factors and cytokines come in. These molecules signal the body’s cells to start repairing damage, much like a foreman directing a construction crew.
Applications of Regenerative Medicine
Now, let’s talk about why regenerative medicine is such a big deal. The potential applications are mind-blowing, and we’re already seeing some real-world success stories.
1. Orthopedics
Injuries to joints, tendons, and ligaments are notoriously difficult to heal. Regenerative therapies like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell injections are already being used to treat conditions like osteoarthritis and sports injuries, helping patients avoid surgery and get back on their feet faster.
2. Cardiology
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide. Regenerative medicine offers hope by using stem cells to repair damaged heart tissue, potentially reversing the effects of heart attacks and chronic conditions like heart failure.
3. Neurology
The brain and spinal cord have limited natural healing capabilities, which makes conditions like stroke, Parkinson’s, and spinal cord injuries particularly devastating. Regenerative therapies are showing promise in restoring lost functions by regenerating neural tissues.
4. Organ Regeneration
One of the most exciting frontiers is growing replacement organs in the lab. While we’re not quite at the point of replacing entire organs like hearts or kidneys, we’ve made significant strides in creating functional parts of organs, such as liver patches and pancreatic islets.
5. Chronic Wounds and Skin Grafts
For patients with burns, ulcers, or other chronic wounds, regenerative medicine offers faster healing and better outcomes. Bioengineered skin grafts and cell-based therapies are already in use.
Why is Regenerative Medicine a Game-Changer?
So, why all the hype? Here are some of the key reasons regenerative medicine is considered a game-changer:
- Reduces Reliance on Transplants: The demand for organ transplants far outpaces supply, leading to long waiting lists and high mortality rates. Regenerative medicine could eliminate this gap by creating tissues and organs in the lab.
- Personalized Treatment: Because many regenerative therapies use the patient’s own cells, the risk of rejection is significantly reduced. This also opens the door to highly customized treatments.
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to traditional surgeries and treatments, many regenerative therapies are minimally invasive, leading to shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
- Addresses Root Causes: Unlike conventional medicine, which often focuses on symptom management, regenerative medicine aims to restore normal function by addressing the underlying cause of the disease or injury.
Challenges and Limitations
Of course, no field is without its challenges. Here are some hurdles regenerative medicine still needs to overcome:
- Cost: These therapies are often expensive, making them inaccessible to many patients. Scaling up production and refining techniques will be key to reducing costs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Because regenerative therapies are so novel, they don’t always fit neatly into existing regulatory frameworks, leading to delays in approval and adoption.
- Technical Challenges: Growing functional tissues and organs is incredibly complex, and there’s still a lot we don’t know about how cells behave in different environments.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of embryonic stem cells and genetic engineering raises ethical questions that society continues to grapple with.
What Does the Future Hold?
The future of regenerative medicine is incredibly bright. With advances in biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and 3D printing, we’re on the cusp of breakthroughs that could redefine healthcare as we know it. Imagine a world where:
- Diabetes is cured with lab-grown pancreatic cells.
- Paralyzed individuals regain mobility thanks to spinal cord regeneration.
- Failing organs are replaced with custom-grown versions, tailored to the individual.
These scenarios might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but they’re closer to reality than you might think.
Final Thoughts
Regenerative medicine is more than just a buzzword; it’s a paradigm shift in the way we approach healing. While there are still challenges to overcome, the progress we’ve made so far is nothing short of astounding. As research continues to advance, the possibilities seem endless.
Whether you’re a patient, a healthcare provider, or just a science enthusiast, it’s an exciting time to watch this field evolve. Who knows? In the near future, we might all benefit from the incredible promise of regenerative medicine.